Draconids 2019: prediction of activity
to the list of predictions
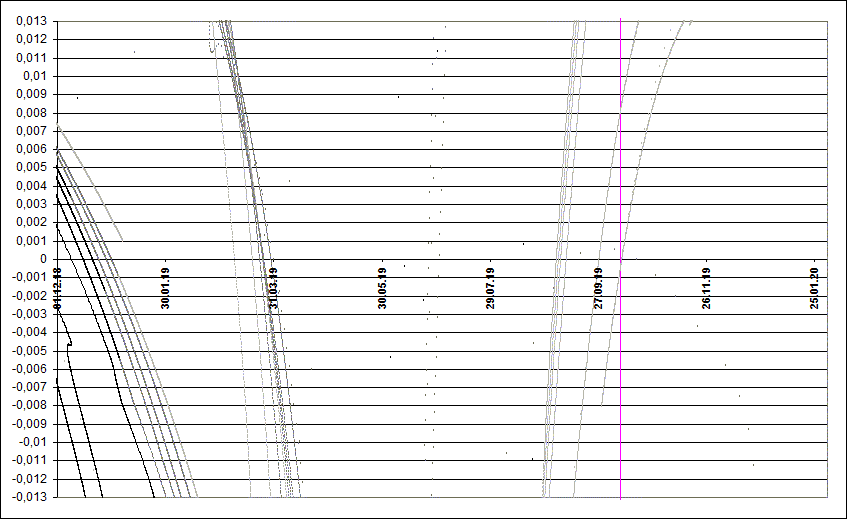
Fig. 1. Space-temporal projection of Draconid trails parts onto their minimal distance passages in 2019 (correspondence between colours of the particles and their ejection velocities can be seen здесь.
In 2019 the Draconids could again show activity a year after expected moderate activity in 2018. This is connected with ecounter between the Earth and 1959 trail, and this encounter is quite similar to 1999 case, when a small activity was detected due to encounter with 1966 trail a year after the shower outburst in the perihelion 1998 year. Paratemers of encountered trails in 1999 and 2019 are given below in the table:
| Year | Maximum date and time, UT | Solar longitude, ° | rD-rE, AU | fM(fMD) | Vej, m/s | Comments |
| 1999 | 09.10.1999 12:24 | 195.776 | -0.00139 | 3.725 | 69.5 | 1966 trail |
| 2019 | 08.10.2019 14:44 | 194.759 | -0.00119 | 2.360 | 62.9 | 1959 trail |
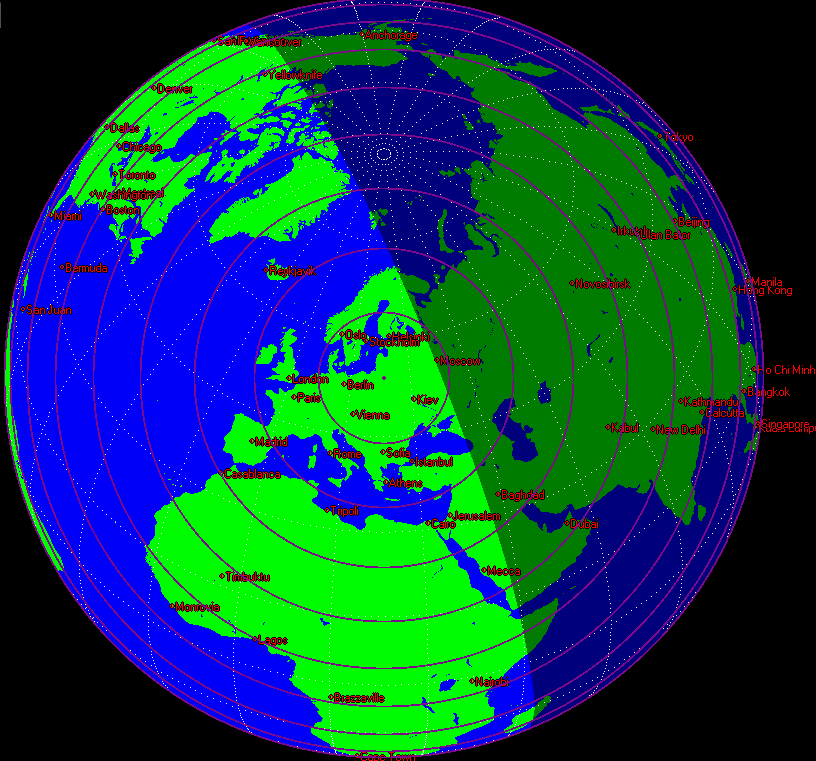
Fig. 3. The Earth as seen from coming Draconid meteors (RA=261.4°, Dec=+53.9°) during the expected maximum time of outburst from 1953 trail at 14:44 UT 8 October.
If happens at expected time, the most favorable conditions for this outburst observing would be in the large areas of Eurasia, up to longitudes of Western Siberia. Unfortunately, the waxing gibbous Moon would be a significant trouble as it will shine in the evening time when the shower radiant is at its highest altitudes in the sky.
Ссылки
1. "Comet's dust 2.0" program by S. Shanov and S. Dubrovsky. [Used for orbital computations.]
2. Lyytinen E, van Flandern T. "Predicting the strength of Leonid outbursts", 2000, Icarus, P. 158-160.
3. Jenniskens P. Meteor showers and their parent comets, 2006, 780 p. 4. Kasuo Kinoshita, http://jcometobs.web.fc2.com/ [Orbital elements of the comet 8P Tuttle]
5. Hewgill G. Xearth 1.1.0 (Software program), 2003. 6. Molau S. Results of the IMO Video Meteor Network – December 2014. http://www.imonet.org/reports/201412.pdf 7. 2016 Meteor Shower Calendar, http://imo.net/files/data/calendar/cal2016.pdf
Ссылки
1. "Comet's dust 2.0" program by S. Shanov and S. Dubrovsky. [Used for orbital computations.]
2. Lyytinen E, van Flandern T. "Predicting the strength of Leonid outbursts", 2000, Icarus, P. 158-160.
3. Jenniskens P. Meteor showers and their parent comets, 2006, 780 p. 4. Kasuo Kinoshita, http://jcometobs.web.fc2.com/ [Orbital elements of the comet 8P Tuttle]
5. Hewgill G. Xearth 1.1.0 (Software program), 2003. 6. Molau S. Results of the IMO Video Meteor Network – December 2014. http://www.imonet.org/reports/201412.pdf 7. 2016 Meteor Shower Calendar, http://imo.net/files/data/calendar/cal2016.pdf